Machine Learning: The Beginner Guide
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables systems to learn and make decisions from data without being explicitly programmed. Instead of following a static set of instructions, ML systems improve their performance through experience.
At its core, ML involves building models that can recognize patterns, make predictions, and adapt to new inputs over time. It is used in applications like spam detection, recommendation systems, language translation, self-driving cars, and medical diagnosis.
“A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T as measured by P improves with experience E.” — Tom M. Mitchell
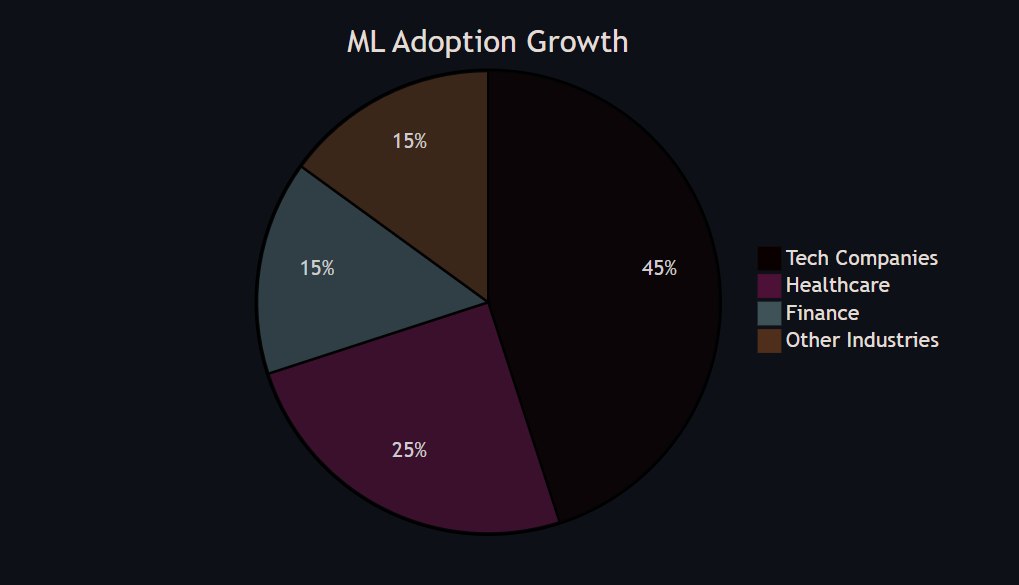
🌟 Why ML Matters Today
Industry Transformation
| Sector | Application | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Early disease detection | 30% more accurate than humans |
| Finance | Fraud prevention | $12B annual savings |
| Retail | Personalized recommendations | +35% conversion rates |
| Manufacturing | Predictive maintenance | 45% fewer breakdowns |
📚 Types of Machine Learning
Machine Learning is broadly categorized into four types based on the kind of learning signal or feedback available to a learning system:
1. Supervised Learning
- Definition: The model is trained on a labeled dataset (input-output pairs).
- Goal: Learn a mapping function from inputs to outputs.
- Examples: Linear Regression, Decision Trees, Support Vector Machines
- Applications: Spam detection, stock price prediction, house price estimation
2. Unsupervised Learning
- Definition: The model is given data without explicit instructions on what to do with it.
- Goal: Discover hidden patterns or groupings in data.
- Examples: K-Means Clustering, PCA, Autoencoders
- Applications: Customer segmentation, anomaly detection
3. Semi-Supervised Learning
- Definition: A mix of labeled and unlabeled data used for training.
- Goal: Use the small amount of labeled data to better leverage the unlabeled data.
- Examples: Self-training, co-training algorithms
- Applications: Image and speech classification where labeling is expensive
4. Reinforcement Learning
- Definition: An agent learns to make decisions by taking actions in an environment to maximize cumulative reward.
- Goal: Learn a policy that maps states to actions.
- Examples: Q-learning, Deep Q Networks (DQNs), Policy Gradients
- Applications: Robotics, game playing (like AlphaGo), recommendation engines
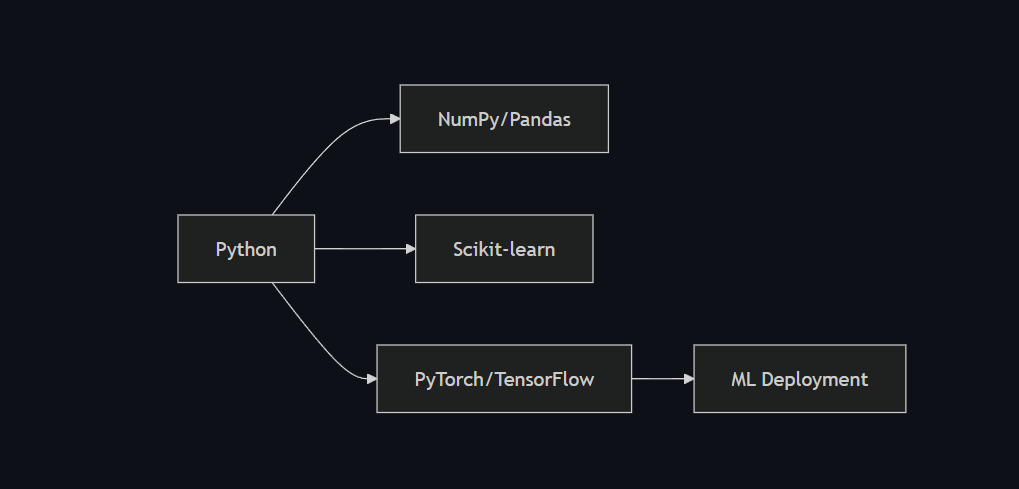
🧰 The ML Toolkit 2025
Essential Stack
Trending Libraries
| Library | Purpose | Stars |
|---|---|---|
| HuggingFace | NLP | 100K+ |
| Ray | Distributed ML | 25K+ |
| MLflow | Experiment Tracking | 15K+ |
| PyTorch Lightning | Simplified DL | 20K+ |
🧭 Fields of Machine Learning
Machine Learning spans several interdisciplinary fields:
- Computer Vision – image classification, object detection, facial recognition
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – language modeling, translation, sentiment analysis
- Time Series Analysis – forecasting stock prices, weather predictions
- Recommender Systems – movie recommendations, product suggestions
- Healthcare & Bioinformatics – disease prediction, drug discovery
- Finance & Risk Modeling – credit scoring, fraud detection
🗺️ Roadmap to Learn Machine Learning (Step-by-Step)
📌 1. Prerequisites
- Basic Python programming
- Linear Algebra: matrices, vectors, dot product
- Statistics: mean, variance, standard deviation, probability
- Calculus: derivatives, gradients (for optimization)
📌 2. Learn Core ML Concepts
- Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning
- Overfitting vs Underfitting
- Bias-Variance Tradeoff
- Evaluation Metrics (Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F1-score)
📌 3. Hands-On With Algorithms
- Linear Regression, Logistic Regression
- Decision Trees, Random Forest, SVM
- K-Means Clustering, DBSCAN, PCA
- Naive Bayes, KNN
📌 4. Use ML Libraries
- Scikit-learn – beginner-friendly ML library
- Pandas/Numpy – data manipulation
- Matplotlib/Seaborn – visualization
📌 5. Build Projects
- Spam email classifier
- Movie recommendation system
- Image classifier (CIFAR-10 or MNIST)
- Sales prediction model
📌 6. Learn Deep Learning (Optional Advanced Step)
- Neural Networks, CNNs, RNNs
- Use TensorFlow and PyTorch
- Study architectures like Transformers
📌 7. Practice and Compete
- Kaggle Competitions
- Google Colab notebooks
- LeetCode (for ML coding practice)
💡 Cutting-Edge Trends
2025 Innovations
- Multimodal AI - Models processing text+images+audio simultaneously
- TinyML - Deploying models on edge devices
- AI-Generated Code - GitHub Copilot X capabilities
- Quantum ML - Quantum-enhanced algorithms
Ethical Considerations
1
2
3
4
+ Model interpretability
+ Fairness audits
- Data privacy risks
- Job displacement concerns
🏆 Pro Tips from ML Engineers
- “Garbage in, garbage out” - Spend 80% time on data cleaning
- “Start simple” - Linear models often outperform complex ones
- “Production ≠ Research” - Monitor model drift
- “Explainability sells” - SHAP/LIME for business buy-in
📌 Final Thoughts
Machine Learning is a journey — start small, build consistently, and deepen your understanding over time. Stay curious, practice regularly, and don’t be afraid to get your hands dirty with real data. 🚀